Artificial intelligence (AI) is a buzzword often surrounded by both hype and skepticism. Some fear that with the rise of AI we have set ourselves on a trajectory where machines could become more intelligent than humans, while others view AI as a panacea for solving all of the complex global problems we currently face. In this blog we will look at the rise of AI, key terms and tools in the field, and how it powers our solutions at Rimm.
A brief history of AI
To fully appreciate the current capabilities of AI, it is worth looking back at its history. Contrary to the popular belief that AI appeared relatively recently as a feat of modern technology, it has actually existed as a field for almost 70 years! In the summer of 1956, a computer scientist named John McCarthy brought together 10 men across two months, to study the possibility of creating a machine that could think like a human. They spent the summer exploring whether machines could use language, form abstractions and concepts and solve problems traditionally reserved for humans. This summer workshop has become widely accepted as the birthplace of AI, and since then there has been significant research and investment in the field. Some major breakthroughs also occurred early on; in 1959 the first self-taught computer was created, in 1966 the first chatbot using natural language processing (NLP) was made, and in 1997 IBMs computer ‘Deep Blue’ beat the reigning world chess champion for the first time, proving the power of machine learning and its propensity for problem solving.
At its core, AI is a collection of algorithms and data-driven models, and these models have seen significant advancements in recent years, particularly in natural language processing, image recognition and predictive analytics. This progress has been driven by improvements in computational power, algorithm design and the availability of large datasets. The AI market is expected to reach $184bn in 2024, with global AI investment predicted to reach over $200bn by 2025.
Breaking down artificial intelligence and how we use it at Rimm
AI can be applied to sustainability in various ways, including emission factors recommendations, sustainability reporting, predictive models and renewable energy management. It can streamline data collection, enhance quality checks and significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of sustainability reports.
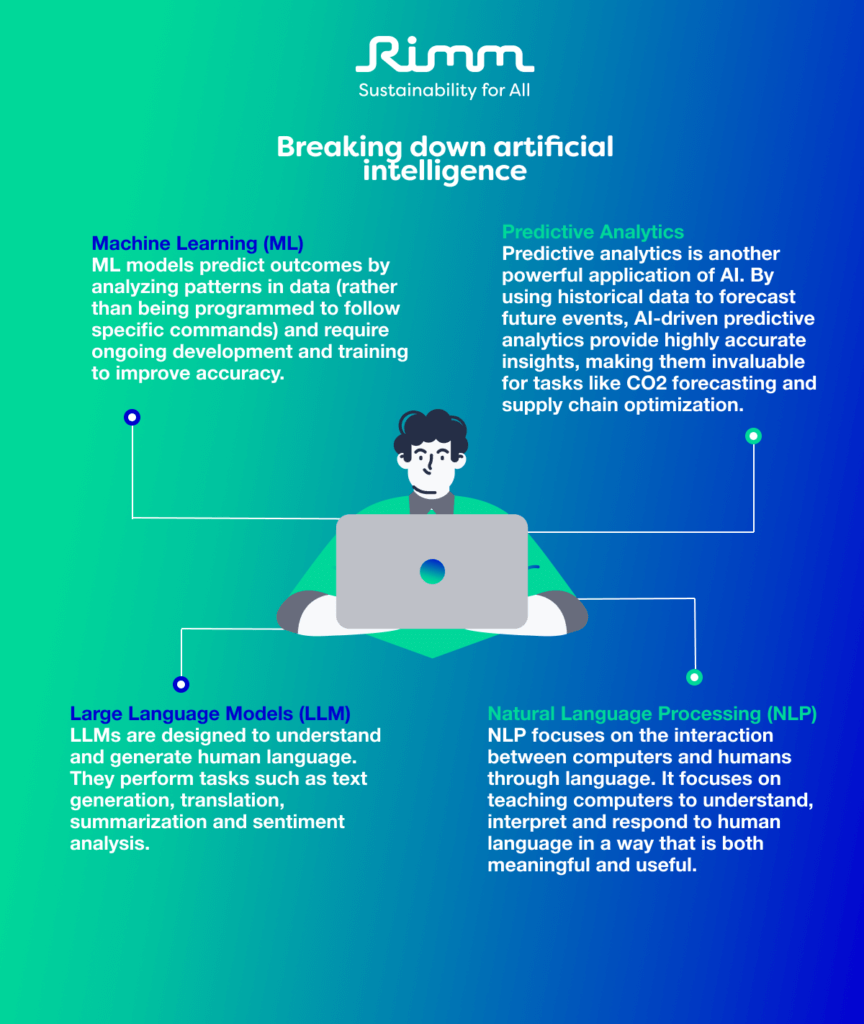
Machine Learning
Machine learning models predict outcomes by analyzing patterns in data (rather than being programmed to follow specific commands) and require ongoing development and training to improve accuracy. Tree-based models, in particular, are state-of-the-art for predictive analytics. At Rimm we use machine learning models that leverage a large number of decision trees, and average predictions to get a numerical result. The models we use are known as ‘ensemble models’ as they use so many decision trees, and we use these for carbon emissions estimation and risk rating estimation.
Natural Language Processing and Large Language Models
Natural language processing (NLP) focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through language. It focuses on teaching computers to understand, interpret and respond to human language in a way that is both meaningful and useful. Our NLP tools streamline data gathering, ensuring comprehensive and accurate datasets. Using tree-based algorithms, we provide precise estimates of carbon emissions and assess and rate risks, enabling better decision-making. Our platform, myCSO, integrates these AI tools to offer a robust solution for managing sustainability initiatives.
One of the key technologies in AI-driven data analysis is Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs are designed to understand and generate human language. They perform tasks such as text generation, translation, summarization and sentiment analysis. With ESG initiatives, LLMs classify text into relevant topics, helping organizations meet sustainability standards.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is another powerful application of AI. By using historical data to forecast future events, AI-driven predictive analytics provide highly accurate insights, making them invaluable for tasks like CO2 forecasting and supply chain optimization. Predictive analytics powers our risk approximation tool – a custom, state-of-the-art machine learning model, predicting risk intervals with a high degree of accuracy (>95%). This model has been trained from scratch using risk data, and can support clients in gaining a better understanding of their risk profile.
At Rimm, our AI-driven solutions empower organizations to not only meet current ESG standards but also proactively shape a more sustainable future. Our platform, myCSO, integrates AI tools to offer a comprehensive solution for managing sustainability initiatives. By leveraging AI, organizations can gain valuable insights from their data, optimize their operations and contribute to a more sustainable world.