Understand the difference between sustainability, ESG and CSR reporting. We’ve made it simple with our basic guide!
Today’s alphabet soup of sustainability jargon and buzzwords is a challenge to navigate. ‘Sustainability,’ ‘ESG’ and ‘CSR’ are often confused and used interchangeably despite having different contextual implications. While there is a considerable overlap in definitions and scopes, replacing one of these key terms with another is inaccurate and misleading.
Let’s unpack these terms…
Sustainability: officially defined in the 1987 United Nations (UN) Brundtland Commission as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” This is the most widely recognized definition of sustainability but can be defined differently depending on context.
Within the business context, sustainability refers to the act of balancing three interconnected pillars: environmental, social and economic. Considering these three pillars, a key endeavor in corporate sustainability is to manage an enterprise in the long term without causing extensive damage to the environment or adopting socially harmful practices.
- The environmental pillar encompasses practices and actions that aim to minimize negative impact on natural ecosystems, support biodiversity and maintain or restore natural resources and climatic cycles.
- The social pillar includes meeting the needs of, supporting and engaging with stakeholders, including communities, employees and consumers.
- The economic pillar seeks to meet the needs of the company by managing risks, maintaining profitability and enhancing resilience.
ESG: a framework that helps measure a company’s sustainability and societal impact, using metrics that matter to stakeholders, particularly investors. It encompasses environmental, social and governance factors that help evaluate a company’s risk exposure with the aim of improving investment decisions.
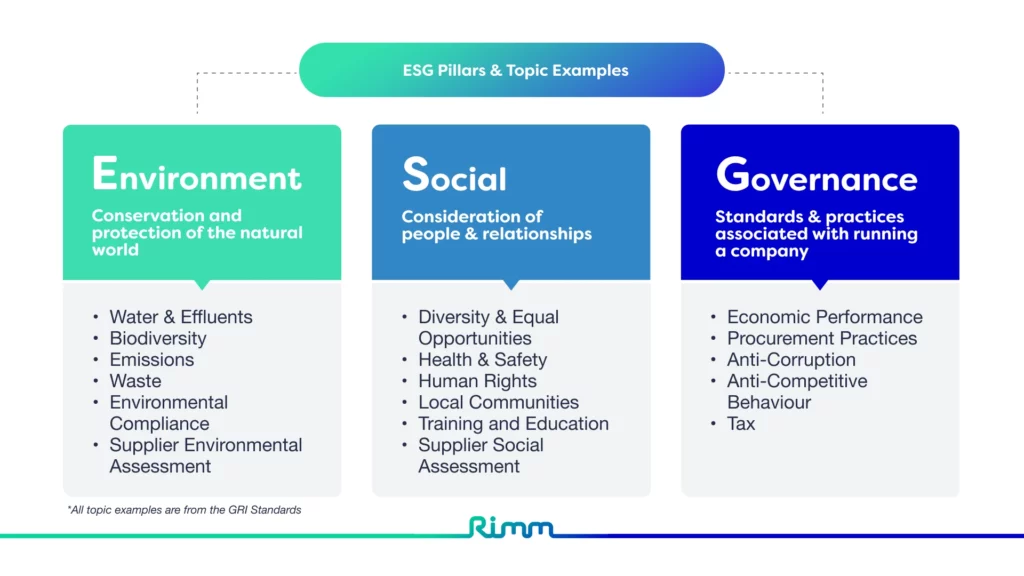
ESG is typically underpinned by a financial motivation by corporates and investors as they seek to improve the valuation of the business.
Incorporating ESG is critical for sustainability reporting and facilitates a structured process that involves conducting a materiality assessment, collecting insights from stakeholders, developing a measurable roadmap and set of key performance indicators (KPIs), setting goals and tracking progress.
CSR: a self-regulating business model promoting companies’ social accountability and engagement in volunteering or ethically-oriented practices. By practicing corporate social responsibility (CSR), companies can be more conscious of their impact on society.
To incorporate good CSR practices, businesses can consider improving its company culture, impact on the environment and relationship with the local community. They can then motivate their employees to be more engaged and become part of the solution.
According to the Corporate Governance Institute, what makes CSR distinct from ESG is its focus on informing stakeholders about the values and goals of the business, including corporate volunteering, reducing carbon footprint and engaging with charities.
Both CSR and ESG can be used by a company simultaneously. CSR provides a framework for the company to communicate internally with employees, while ESG provides measurable goals.

Simplify Your Sustainability Performance & Tracking With myCSO
✅ Calculate your scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions instantly
✅ Gauge your company’s sustainability performance
✅ View your sustainability performance all from one dashboard
✅ Benchmark against industry peers
Enter your information below to book a demo with our team today.